Have you ever looked at a conversion path report in Google Analytics 4? Here it is for one of our clients for last month:
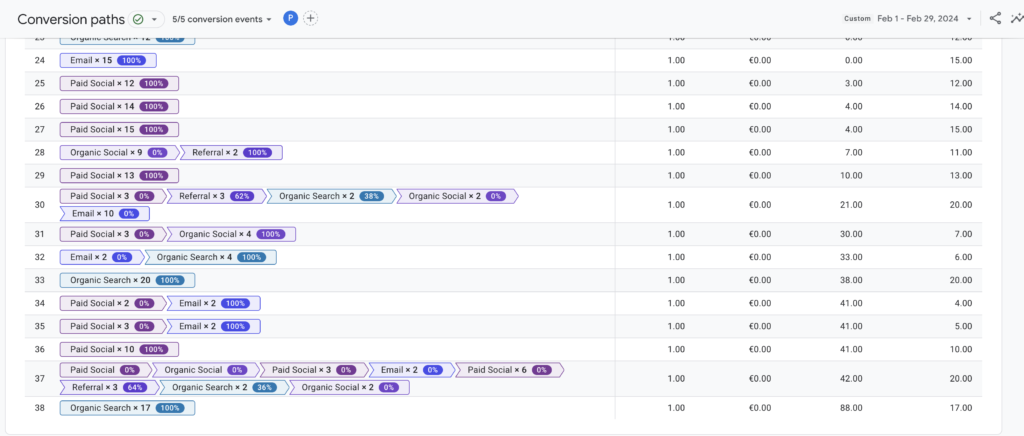
What this shows is the different patterns of visits that users take before completing a conversion action in the website.
The path length varies by website but it is rare that we come across a website that typically has users converting on their first visit consistently. As you can see above there are many people taking 10+ visits to the website before making a commitment.
So – this raises the topic of conversion attribution. If you are running paid ads and those ads are contributing in part to a conversion action but not wholly then how should you calculate the ROI or the distribution of the lead/sale value?
Additionally, within a paid channel such as Google ads, there are many cases where a user will click on 2 or 3 paid ads for the same website before committing, so how do you divide the value of that conversion between those clicks so that you can determine the return on ad spend for each keyword? Is the first click most significant? The last click? Or all clicks equally etc?
Attribution models in Google Ads refer to the rules or methodologies used to determine how credit for conversions is assigned to different touch points in the customer’s journey. In digital advertising, a customer’s path to conversion can involve multiple interactions with ads and various channels before completing a desired action, such as making a purchase or filling out a form.
Until late 2023, Google Ads provided the below attribution models that advertisers could choose from to analyse and understand the impact of different touch-points in the conversion process. Each model had its own set of rules for assigning credit, allowing advertisers to gain insights into which ads and keywords contribute most significantly to conversions. But with the rise of Google’s AI based automated bidding, most of the attribution models have been removed except the last click and data-driven attribution models because these models didn’t provide the flexibility needed to adapt to evolving consumer journeys.
- Last Click Attribution (still available):
- Assigns full credit for a conversion to the last interaction (click) that led to the conversion.
- First Click Attribution (not available):
- Assigns full credit for a conversion to the first interaction (click) in the customer journey.
- Linear Attribution (not available):
- Distributes credit equally among all interactions throughout the conversion path.
- Time Decay Attribution (not available):
- Gives more credit to interactions closer in time to the conversion, with diminishing credit for earlier interactions.
- Position-Based Attribution (not available):
- Assigns 40% credit each to the first and last interactions, with the remaining 20% distributed evenly among middle interactions.
- Data-Driven Attribution (available):
- Utilizes machine learning to analyse conversion paths and dynamically assigns credit based on the actual impact of each interaction.
Below figure further simplifies each model.
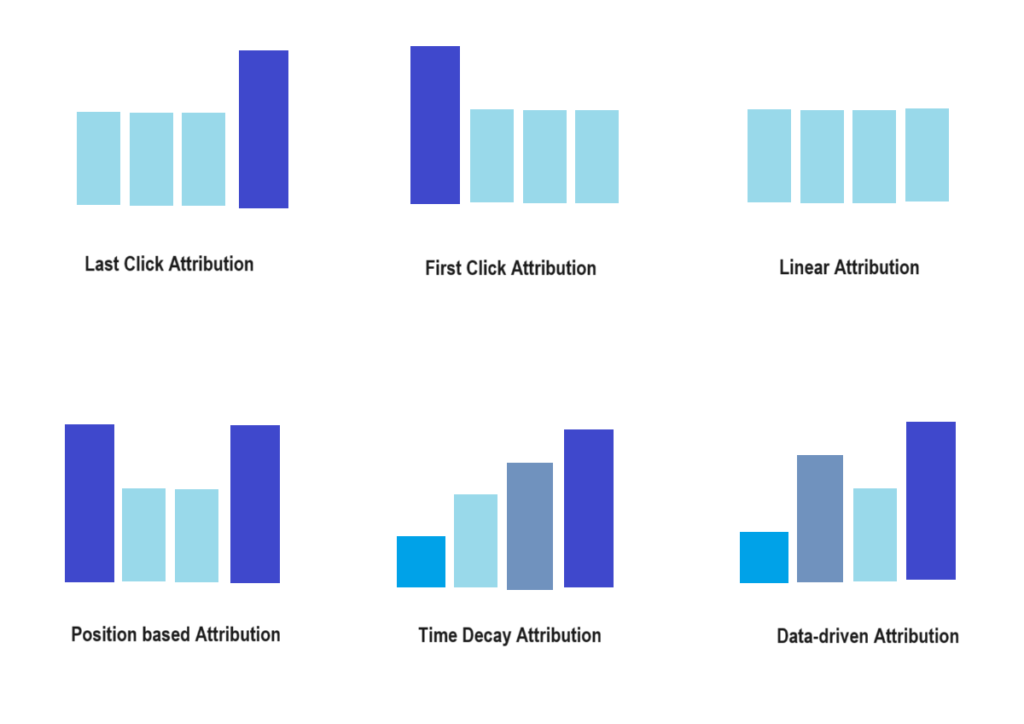
The Data-Driven Attribution Model is distinguished by its sophisticated approach to assigning credit to various touchpoints in the customer journey. This model leverages machine learning algorithms to analyse vast datasets, identifying patterns and trends in user behaviour. Unlike static models, the data-driven approach is dynamic and adaptive. It continuously learns and adjusts its attribution rules based on evolving user behaviour.
Eligibility
Access to the Data-Driven Attribution Model is subject to eligibility criteria based on the amount of data available in your Google Ads account. In general, the conversion actions need at least 300 conversions and 3,000 ad interactions across all Google ads platforms (search, display, youtube, shopping etc.) within 30 days to be eligible. Once you’re using data-driven attribution for these conversion actions, you won’t be able to continue using this model if your data drops below 2,000 ad interactions across all Google ads platforms or below 200 conversions for the conversion action within 30 days. You’ll receive an alert when your data drops below this level. After 30 days of continued low data, your conversion action will be switched to the “Last click” attribution model.
How Data-Driven Attribution Works
The working mechanism of the Data-Driven Attribution Model can be broken down into a few key steps:
- Data Collection: Google Ads collects and processes data on user interactions (such as clicks and video engagements on search, shopping, display etc., user behaviour on the website, conversions data) with your ads and website.
- Machine Learning Analysis: The machine learning algorithm analyses this data, identifying patterns and relationships between different touchpoints in the customer journey. It looks at factors such as devices, time of the day, day of the week, geographic location to understand what drive conversions.
- Credit Assignment: Based on the analysis, the model assigns credit to each touchpoint, considering its actual influence on conversions. It provides a more nuanced and accurate representation of the customer journey.
- Adaptability: One of the standout features is its adaptability. As user behaviour evolves, the model continues to refine its attribution rules, ensuring ongoing accuracy.
Let’s understand this with an example.
An ecommerce furniture brand has the primary goal of selling sofas online using Google Ads. Data-driven attribution model collects and analyses all the data including clicks, user behaviour on the website, conversions data etc. and finds that users who first search for sofa colours with fabric types, such as ‘red velvet sofa’, and later click on a brand keyword, were the most likely to purchase. Whereas users who search for keywords without colours and fabrics like ‘discount sofa’ and ‘handmade sofa’ first and then click on brand keywords are the least likely to convert. This results in Data-Driven Attribution assigning more credit to colour related keywords, ad groups and campaigns. Now, when you look at data and reports in your account, you have more complete and valuable information.
Benefits
The adoption of the Data-Driven Attribution Model comes with several advantages:
- Precision in Attribution: By considering the actual impact of each touchpoint, the model provides a more precise understanding of which keywords, ads, ad groups and campaigns contribute to conversions.
- Optimised Budget and Bids Allocation: Marketers can allocate their budget and bids more effectively, focusing on channels and touchpoints that truly contribute to conversion outcomes. If you use an automated bid strategy to drive more conversions, your bidding will use this important information to help you get more conversions.
- Insights for Strategy Refinement: Detailed insights derived from the model can inform strategic decisions, helping marketers refine their advertising strategies for maximum impact.
How to Set Up Data-Driven Attribution
Ensure that your account meets the eligibility criteria, primarily having a sufficient volume of conversion data.
Step 1 – Click on ‘Measurement’ under ‘Tools and settings’ and then click on ‘Conversions’.
Step 2 – Click on the conversion action you want to set up the data-driven attribution model to.
Step 3 – Click on ‘Edit Settings’.

Step 4 – Under ‘Attribution’, select ‘Data-driven’. Click on ‘Save’.

Understanding the dynamic Data-Driven Attribution Model, equips advertisers with powerful insights to optimise campaigns. Whether leveraging the traditional last click model or embracing innovative data-driven model, the key lies in decoding the customer journey. Armed with this knowledge, advertisers can strategically allocate budgets and propel their campaigns towards success in the ever-competitive digital landscape.

